The Internet of Things (IoT) has reshaped our world, embedding smart capabilities into everyday objects — from thermostats and security cameras to factory robots and self-driving cars. But as IoT devices grow in number and complexity, traditional cloud-based data processing struggles to keep up. Enter edge computing, a powerful solution that’s redefining how IoT systems operate.
What Is Edge Computing in IoT?
Edge computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to where it is generated — that is, at the edge of the network — rather than sending it to a distant cloud server. This localized data handling means IoT devices can respond faster and operate more efficiently, especially in environments where speed and reliability are critical.
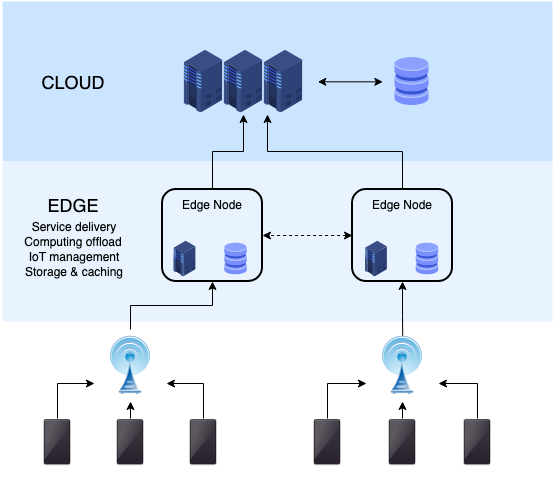
Image source: Wikipedia
Why Cloud-Only Isn’t Enough Anymore
In a typical IoT setup, data travels from sensors to the cloud, where it’s analyzed and decisions are made. While this works for many use cases, it creates issues for real-time applications:
- Latency: Sending data to the cloud takes time. For applications like self-driving cars or robotic surgery, milliseconds matter.
- Bandwidth: With billions of IoT devices online, cloud bandwidth is under strain.
- Reliability: A slow or broken internet connection can paralyze cloud-dependent devices.
- Privacy: Sensitive data sent to centralized servers is more vulnerable to breaches.
Edge computing solves these by processing data locally, reducing delay, and even enabling offline functionality.
How Edge Computing Works with IoT Devices
Edge computing integrates directly into IoT systems via:
- Edge Gateways: These act as mini data centers near the data source, handling tasks like filtering, analysis, and routing.
- Smart Sensors and Devices: Increasingly, sensors themselves are becoming intelligent enough to process data without external help.
- Fog Computing Layers: Sometimes, a middle layer (fog computing) bridges the gap between edge devices and the cloud for more robust architectures.
The result is faster decisions, less traffic, and greater autonomy.
Key Applications of Edge Computing in IoT
- Smart Homes and Buildings
Think motion-sensing lights that react instantly, voice assistants that don’t lag, or HVAC systems that adjust in real time. With edge computing, response times are immediate — no cloud delay. - Industrial IoT (IIoT)
In factories, edge devices monitor machines, predict failures, and prevent costly downtime — all in real time. This is known as predictive maintenance. - Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on cameras, radar, and sensors. Processing this massive data set locally helps the vehicle make split-second decisions without relying on cloud access. - Healthcare
Wearables and hospital monitors analyze patient vitals instantly, alerting staff if something goes wrong. Edge computing can literally save lives. - Agriculture
Smart irrigation systems, weather sensors, and livestock monitors use edge AI to optimize farming operations in areas with limited connectivity.
Benefits of Edge Computing for IoT
- Speed: Decisions are made in milliseconds.
- Reduced Costs: Less data sent to the cloud = lower bandwidth and storage costs.
- Security: Local processing minimizes data exposure.
- Scalability: New devices can be added without overwhelming central systems.
- Resilience: Devices continue working even when cloud access is down.
Challenges to Consider
- Hardware Costs: Edge-capable devices are often more expensive.
- Maintenance Complexity: Managing many local nodes can be harder than a centralized cloud.
- Standardization: With diverse vendors, compatibility is an ongoing issue.
Still, the benefits far outweigh the challenges — especially as the technology matures.
The Takeaway
Edge computing is no longer just a buzzword. It’s a fundamental shift in how IoT devices operate, making them smarter, faster, and more reliable. Whether it’s a smart thermostat in your living room or an autonomous drone in a disaster zone, edge computing is powering the next generation of IoT.
IoT Trends to watch in 2025
- IoT for Beginners: The Complete Smart Home Starter Guide (2025 Edition)
 Smart home devices are no longer sci‑fi toys for tech geeks – they are affordable, easy to install, and can genuinely make everyday life more convenient, efficient, and secure. This guide walks you through the essentials of getting started with IoT and building a smart home in 2025 without getting overwhelmed by buzzwords and acronyms.…
Smart home devices are no longer sci‑fi toys for tech geeks – they are affordable, easy to install, and can genuinely make everyday life more convenient, efficient, and secure. This guide walks you through the essentials of getting started with IoT and building a smart home in 2025 without getting overwhelmed by buzzwords and acronyms.… - Designing a Smarter Home in 2026: What People Get Wrong About Automation
 Smart homes were once science fiction, but today they’re a reality in millions of households. With voice assistants, smart plugs, and automated lighting systems, it’s easy to assume home automation is simply a matter of plugging in a few devices. Yet, many homeowners quickly discover that “smart” doesn’t always mean simple. In this article, we’ll…
Smart homes were once science fiction, but today they’re a reality in millions of households. With voice assistants, smart plugs, and automated lighting systems, it’s easy to assume home automation is simply a matter of plugging in a few devices. Yet, many homeowners quickly discover that “smart” doesn’t always mean simple. In this article, we’ll… - Automated Online Trading: How IoT is Redefining Financial Markets
 Introduction automated online trading In a world where milliseconds can decide millions, the fusion of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and automated online trading is reshaping global finance. What once relied solely on human judgment now increasingly depends on connected machines, real-time data, and predictive algorithms. From weather sensors influencing agricultural trades to smart logistics…
Introduction automated online trading In a world where milliseconds can decide millions, the fusion of Internet of Things (IoT) technology and automated online trading is reshaping global finance. What once relied solely on human judgment now increasingly depends on connected machines, real-time data, and predictive algorithms. From weather sensors influencing agricultural trades to smart logistics… - The Role of Linux in IoT: Powering the Connected World
 The Internet of Things (IoT) is everywhere—from smart homes and wearable devices to industrial automation and self-driving cars. Behind the scenes, one operating system plays a surprisingly dominant role: Linux. Known for its stability, flexibility, and open-source nature, Linux has become the backbone of countless IoT devices and platforms. But what makes Linux so well-suited…
The Internet of Things (IoT) is everywhere—from smart homes and wearable devices to industrial automation and self-driving cars. Behind the scenes, one operating system plays a surprisingly dominant role: Linux. Known for its stability, flexibility, and open-source nature, Linux has become the backbone of countless IoT devices and platforms. But what makes Linux so well-suited… - The Smart Home Revolution in 2025: How IoT is Transforming Everyday Living
 In the past decade, the vision of a truly smart home has moved from futuristic fantasy to everyday reality. As we step into 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) has matured into a robust ecosystem, connecting appliances, security systems, lighting, and even entertainment devices under one seamless digital roof. The result? Homes that are safer,…
In the past decade, the vision of a truly smart home has moved from futuristic fantasy to everyday reality. As we step into 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) has matured into a robust ecosystem, connecting appliances, security systems, lighting, and even entertainment devices under one seamless digital roof. The result? Homes that are safer,…